Everything you need to know about PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) in construction will be explained here. As a civil engineer with 5 years of experience, I’ve encountered the use of PCC multiples of time in various types of buildings and for different purposes, and I’m here to share that practical knowledge with you.
What is PCC and do we really need PCC in construction projects?
The PCC stands for the plain cement concrete which is a mixture of cement, fine aggregate (sand) and coarse aggregate (crushed stone or gravel) with some amount of water.
How to calculate the concrete quantity for the footing?
How To Calculate Quantity of Steel Using Unit Weight of Steel bars?
Shivalik Curv: The Twisted Marvel Redefining GIFT City’s Skyline.
Top 10 Civil Engineering Software Tools in 2025.
What is PCC?
PCC stands for Plain Cement Concrete. It is a mixture of cement, sand, and coarse aggregates mixed with water, without any steel reinforcement. It is mainly used to provide a level surface and a firm base to structural members like footings, columns, and flooring. Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) is one of the most fundamental and commonly used materials in construction. It serves as a strong and durable base for structural elements and is essential for leveling and strengthening the ground before any reinforcement is placed.
Purpose of PCC in Construction
The purpose of PCC is clearly known as it is used for the surface leveling for other main work like flooring, footing, grade slab etc. here we have discussed some of them as below :

- To create a smooth and firm base for reinforcement or formwork for the foundation, footing base, concrete grade slab, etc.
- To prevent direct contact between the reinforcement and soil (which can be corrosive).
- To increase the durability of structural elements by avoiding moisture penetration from the soil.
- To act as a leveling pad for foundations and footings.
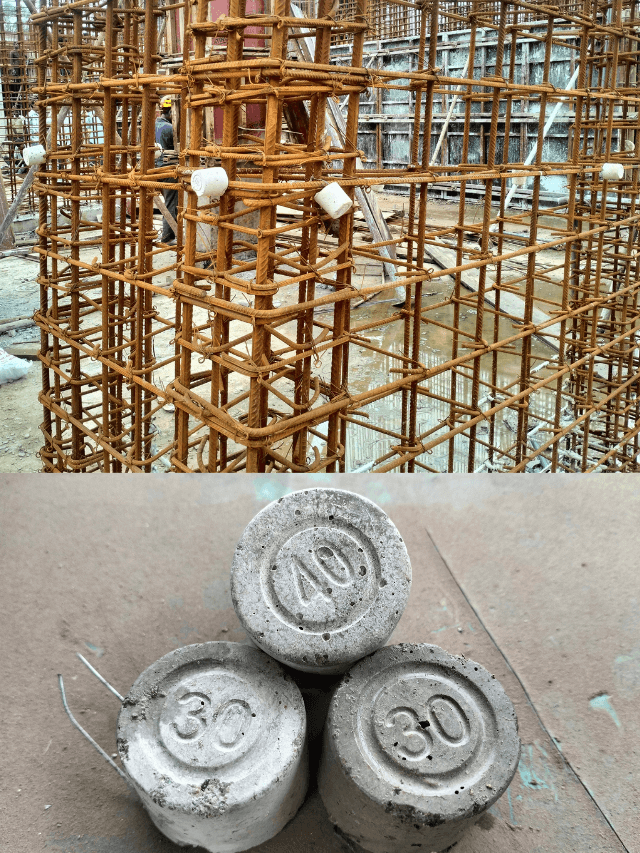
PCC Material Ratio :
Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) is a simple mixture used in areas where there is no direct load or structural strength requirement. In practice, engineers design PCC based on the site’s needs and conditions. According to Indian Standards, commonly used concrete grades for PCC include M5, M7.5, M10, and occasionally M15, if specified by the structural designer. Engineers design PCC based on functional requirements, with mix grades and ratios standardized under IS 456:2000 (Indian Standard).
Common mix ratios:
| Types of Concrete | Grade of Concrete | Mix Ratio (Cement : Sand : Aggregates) | Characteristic strength of cube at 28 days N/mm2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Concrete | M5 | 1:5:10 | 5 |
| Ordinary Concrete | M7.5 | 1:4:8 | 7.5 |
| Ordinary Concrete | M10 | 1:3:6 | 10 |
| Ordinary Concrete | M15 | 1:2:4 | 15 |
| Ordinary Concrete | M20 | 1:1.5:3 | 20 |
| Standard Concrete | M25 | 1:1:2 | 25 |
| Standard Concrete | M30 | Design Mix | 30 |
| Standard Concrete | M35 | Design Mix | 35 |
| Standard Concrete | M40 | Design Mix | 40 |
| Standard Concrete | M45 | Design Mix | 45 |
| Standard Concrete | M50 | Design Mix | 50 |
| Standard Concrete | M55 | Design Mix | 55 |
| High Strength Concrete | M60 | Design Mix | 60 |
| High Strength Concrete | M65 | Design Mix | 65 |
| High Strength Concrete | M70 | Design Mix | 70 |
| High Strength Concrete | M75 | Design Mix | 75 |
| High Strength Concrete | M80 | Design Mix | 80 |
Water-cement ratio is usually kept around 0.4 to 0.5, depending on the site condition and mix.
Note: These are nominal mix ratios used for small-scale works. For structural or large-scale concrete, design mix is preferred as per IS 10262.
Applications of PCC :
Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) can be classified based on its application into two main categories: non-structural and structural use. For non-structural purposes, PCC is widely used as a base or leveling layer. In structural applications, it is only suitable for small-scale projects where the load is minimal. For large and heavy construction projects, PCC is not recommended for structural elements due to its lack of reinforcement.
Below are some of the most common and recommended uses of PCC in construction:

- Flooring base in buildings and industrial areas.
- Flooring for sheds or non-load bearing areas
- To make Paving and walkways.
- Bed concrete for canals or culverts Foundation bedding for footings and columns.
- Levelling pad for formwork installation.
- Levelling flat surfaces for the tiles bed or flooring.
- Surface making for the grade slabs or trimix layers.
Also read,
Foundation in Construction: An Introduction to Their Purpose and Importance.
Comprehensive Guide to the Types of Foundations in Construction.
Steps to Apply PCC at Site :
A step-by-step guide for placing Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) can be followed as outlined below:

- Excavation and site leveling.
- Compaction of soil.
- Formwork placement (if required).

- Mixing and pouring PCC.
- Leveling and compacting concrete surface.
- Curing the PCC for at least 7 days.

Advantages of PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) :
- PCC requires simple tools and techniques, making it easy to mix and place on site without complex machinery.
- It provides a strong and even surface for structural elements, which increases the durability and overall strength of the construction.
- It acts as a barrier, preventing direct contact of reinforcement with soil and moisture, reducing the chances of corrosion and increasing the life of RCC components.
- Since it doesn’t require steel reinforcement, it is cheaper and requires fewer labor resources compared to reinforced concrete.
- It offers a flat base which helps in accurate alignment and placement of reinforcement and formwork in structural work.
- It prevents direct interaction between soil and the structure, reducing the risk of chemical reactions or settlement issues.
- It helps in minimizing the upward movement of moisture through capillary action from the ground to the superstructure.
- It provides a firm and stable base layer for footings, flooring, and other structural components.

Plain Cement Concrete for Structural Members (Small-scale) :-
So we have seen many things about it but sometimes it can be used for the structural members also. When the structure is designed for the low load bearing structures than we can use it such as :
- Strip footings for compound walls or boundary walls,
- Bed concrete under stone masonry
- Light foundation works in rural or temporary structures.
The suitable grade of the concrete may be used as M10 and M15 if not mentioned.
At the end, I hope you may get the little bit of knowledge and practical use of the plain cement concrete. As it is a simple but most fundamental and effective material required at the site. Have you encountered with it? Comment it below if you have any questions regarding the PCC.
Also read,
How To Calculate Quantity of Steel Using Unit Weight of Steel bars?
Comprehensive Guide to the Types of Foundations in Construction.
Excavation in Construction: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Process & Types.
Introduction to Civil Engineering: What It Is and Why It Matters.




















Hello.This post was extremely motivating, especially because I was investigating for thoughts on this subject last Saturday.